Talent management is a massive driving force behind competitive and successful organizations. For HR professionals, it goes beyond the standard remit of recruitment. It involves a strategic approach to the attraction, hiring, development, engagement and retention of top talent.
This guide deep-dives into all areas of talent management. We’ll cover talent management types, its associated terms and benefits, how it can be used as well as its best practices, and examples that you can use to ensure your organization’s talent management strategy is allowing the business to operate at its best.
What is talent management?
Talent management is the strategic process of attracting, developing, retaining and optimizing an organization’s workforce to achieve wider business goals while aligning with employee needs.
The process is broad and far-reaching, and involves identifying and nurturing individuals with potential to do more to ensure they can contribute effectively and are placed in roles that maximize their skills — essentially: to ensure that the right talent is in the right place at the right time.
Key components of talent management include recruitment, onboarding, performance management, learning and development, career planning, and succession planning. Talent management enables organizations to invest in their workforce, contributing to competitive advantage and continuous improvement.
Why is talent management important?
Talent management is too large an area for HR to ignore. With measurable benefits across many areas of the employee lifecycle, a carefully planned-out talent management strategy can bring numerous advantages to an organization’s performance.
Here are five of the most powerful:
Aligning workforce goals with business objectives
One of the most important reasons why talent management is important is because it’s a great way to align an organization’s workforce to its strategic objectives. Indeed, by identifying the skills, knowledge and positions needed to achieve organizational targets, leaders and HR teams are able to deploy talent in the right way.
This is, of course, a win–win process, as employees will benefit from clarity about their roles and responsibilities, while it also helps them understand how what they do contributes to organizational overall success. When this is understood, employees are often more productive, motivated and happy at work through seeing their purpose as well as meaning when at work.
Attracting and retaining top talent
Many labor markets are exceptionally competitive, and organizations will find it challenging to not only attract but also retain the best candidates. Talent management incorporates many strategies to contest this, such as employer branding, competitive compensation packages, as well as robust onboarding programs.
These interventions can help organizations stand out as desirable employers. Employees, meanwhile, benefit from these talent management processes through being able to thrive in supportive work environments where they feel they’re valued and recognized.
Employees can grow through having career development plans, mentoring opportunities and targeted recognition systems, all of which allows them to visualize a future in the organization, thus remaining loyal to where they are.
Building a resilient, future-ready workforce
In an era of change, talent management helps organizations create resilient workforces through a culture of continuous learning, conflict resolution strategies, as well as proactive succession planning. This ensures organizations can remain agile and ready for any and all challenges.
A prepared organization provides stability and even reassurance for employees. Knowing their employer values longer-term development and is thinking ahead will boost engagement and discretionary effort. They will also benefit from succession planning as well as continuous learning opportunities.
Enhancing employee engagement and productivity
Organizations benefit through improves engagement through higher levels of innovation as well as improved efficiency. Employees who are engaged at work are likelier to perform at their best and contribute powerfully to the organization’s success.
A key component of talent management is focusing on building an engaging work environment through things like continuous feedback, skill development, and recognition. Employees seek working environments where their contributions are appreciated and where their growth is prioritized.
This creates a positive working environment that encourages discretionary effort as well as collaboration — outcomes that truly benefit every stakeholder.
Supporting employee development and growth
Organizations that invest strategically in employee growth are well-placed to create an adaptable and even capable workforce. Talent management is the driving force behind effective learning and development interventions, providing employees with opportunities to not only enhance their skills but also drive their careers forward.
For employees, these L&D opportunities mean that talent management can provide them with personal and professional growth. They will also be likely to feel more valued for their potential. Clear career development discussions and established career paths can boost their confidence and satisfaction. It’s really a win–win!
Talent management terms and concepts
Talent management is a broad area of HR and, as such, there are many different terms and concepts to make sense of. This section covers a list of the main talent management definitions to help you get started in pulling a talent management strategy together:
360-degree feedback
A performance review method where employees receive feedback from their peers, subordinates, supervisors and, sometimes, clients.
Career development
The process of planning as well as managing employee growth within the company through various training interventions.
Competency framework
A structured approach to define and measure the skills, knowledge and behaviors that are required for certain roles within the organization.
Competency mapping
The process of identifying the specific skills, knowledge and abilities that are required for different roles so that workforce capabilities can align to organizational goals.
Diversity and inclusion (D&I)
Efforts to create a workplace where people from different backgrounds feel, among other things, valued, respected and included.
Employee engagement
The level of an employee’s commitment, motivation as well as emotional connection to their organization, and how likely they might be to undertake discretionary effort.
Employee experience (EX)
The sum of an employee’s perceptions and interactions within an organization, from recruitment to exit.
Employee retention
Strategies and practices to keep talented employees within the organization, as well as reduce turnover rates.
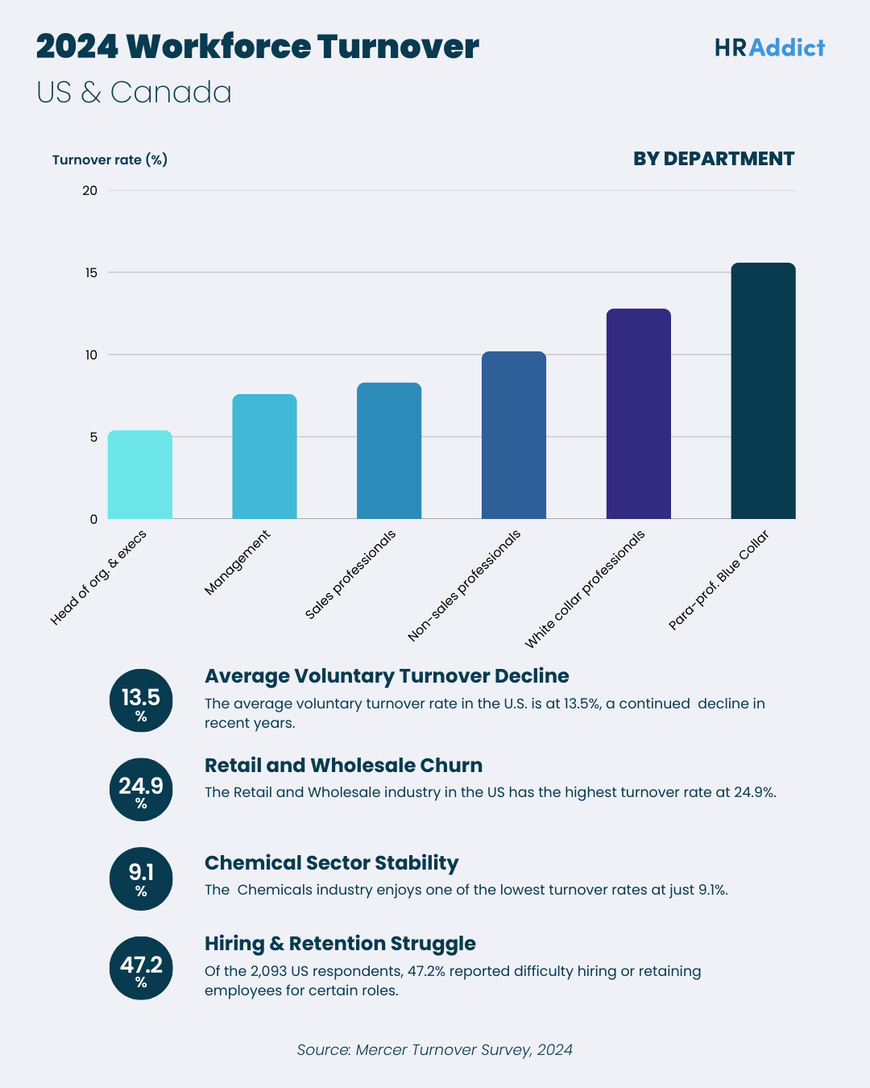
Here is an infographic we created of key workforce turnover rates based on Mercer findings:
Employee value proposition (EVP)
The unique, varied set of benefits and values an organization offers employees in direct exchange for their skills and commitment.
Employer branding
The process of promoting the organization as a desirable place to work in order to attract and retain top talent.
Gamification
Incorporating game-like elements into talent management processes to boost engagement and motivation.
High-potential employees (HiPos)
Individuals identified as having the judgment, drive and interpersonal skills to excel in leadership positions or other key roles within the organization.
Learning and development (L&D)
Programs and initiatives that are aimed at improving employees’ skills and knowledge, with a view to enhancing their performance as well as career progression.
Onboarding
The process of ensuring new employees land well in the organization, including helping them understand their role, the company culture as well as expectations.
Performance management
The continuous process of assessing and improving employee performance using feedback, goal setting as well as performance reviews.
Recruitment
The end-to-end process of sourcing, attracting as well as selecting candidates to fill open roles in the organization.
Succession planning
The process of identifying, calibrating and developing internal talent to fill key roles and hard-to-fill positions in the organization’s future.
Talent management software (TMS)
Digital platforms designed to streamline various talent management processes such as recruitment, onboarding, performance evaluations, and learning and development.
Total rewards
A complete package of compensation, benefits, recognition and other incentives that organizations use to attract and retain employees.
Workforce planning
Actions taken to ensure the organization has the right number of employees with the right skills at the right time.
Talent management strategy and process
Developing a talent management strategy process is a comprehensive piece of work that doesn’t happen by accident. Mapping out your process is essential to its success and for building talent management into the strategic framework of the organization.
Below are five steps for developing a talent management process:
Workforce planning and analysis
Creating a talent development process begins with workforce planning and analysis. This is a critical foundational step that involves, among other things, evaluating the current talent pool, identifying skill gaps and forecasting future talent needs based on the organization’s strategic requirements. It’s important to understand the skills required now, as well as how the organization evolves.
Workforce planning interventions also include looking at external factors that impact the organization, such as technological advances, demographic shifts and wider industry trends, all of which impact future talent needs. Once these needs are identified, companies can tailor hiring programs and development pathways to address the requirements of the business.
Recruitment and talent acquisition
Talent acquisition is the cornerstone of every talent management strategy. This isn’t just concerned with filling open roles but also with creating an employer brand geared towards attracting the right candidates, as well as those who fully align with the organizational culture.
A mix of strategies is used to this effect, such as employer branding, job postings, recruitment agencies and employee referral programs. DEI must also be built into hiring needs as a diverse workforce will bring fresh perspectives, innovation and creativity in a way that drives competitive advantage.
Underpinning talent acquisition initiatives should be a data-driven approach such as applicant tracking systems to objectively assess potential and in-place talent.
Onboarding and employee integration
Once the right talent is hired, the next step is ensuring an effective and efficient onboarding experience for them. This is crucial for integrating new employees into the company in the right way, introducing them to the culture, helping them understand their roles, and setting clearly defined expectations.
A strong onboarding process will also drive engagement, socialization, and make employees feel they’re welcome. Onboarding processes should include mentorship, interaction and plenty of training in a way that equips employees with all the tools they need to succeed.
Getting this right sets up talent for long-term success with the organization.
Performance management and development
An ongoing system of performance management ensures the continued success of your talent. This step involves setting clearly defined performance management expectations, providing regular feedback, as well as proactively identifying areas for supplementary employee development. This will include a structured performance review process, with personal and professional goal-setting built into it.
Performance development must also include training and development, such as provision of learning opportunities through formal workshops, and on-the-job learning. HR and leadership should establish competency guides and clear career paths that will ensure that employees understand how they can grow within the business.
Succession planning and retention
The final step of the talent management process is powerful succession planning. This focuses on identifying and preparing high-potential employees to assume future roles in the company, ensuring leadership continuity.
As part of this process, retention strategies should also be prepared, including offering and evaluating competitive reward programs, with a focus on employee engagement. Higher talent retention rates reduce turnover costs and help to keep the organization stable, again, contributing to long-term growth and success.
Talent management best practices
In this section, we’ll cover some talent management best practices that will help you get the most out of your strategy and stay ahead of the game in how you look after your most talented people.
Aligning talent management with business strategy
A critical talent management best practice is to ensure your efforts are in constant alignment with the company’s overall organizational objectives. This ensures you attract, develop and retain employees with the right skills and who also are a good fit to the organizational culture. To this end, HR teams should work with leadership to understand the organization’s vision, goals, priorities and challenges.
This information can then be used to create a talent management strategy that supports these areas. HR professionals would do well to keep in mind that these areas might change from time to time, and so regular strategic reviews of the talent management strategy will be needed. For example, the needs of a newly established company will be very different from one that has matured and is in a much more stable place.
Focusing on employee wellbeing and work–life balance
Talent management works hand in hand with wellbeing and work–life balance, creating a holistic approach that, among other things, balances professional development with physical, mental, emotional and social wellbeing. This leads to higher levels of job satisfaction and productivity, and reduces the risk of stress or job burnout.
Businesses can implement these initiatives through offering flexible hours, remote work options, and wellness initiatives like mental health resources, employee assistance programs or fitness memberships. Employers that openly communicate what they do to focus on wellness will also see their employer brand becoming stronger and better known as well.
Fostering a culture of feedback and continuous improvement
Nurturing a culture of feedback and continuous improvement is essential for ensuring employees remain upskilled, engaged and laser-focused on their goals. Whereas a structured performance review process is useful, this shouldn't be limited to end-of-year reviews. Instead, ongoing and two-way feedback is central to success.
HR teams should coach managers on providing motivational feedback to employees that’s focused on strengths and development areas. Employees, meanwhile, should be encouraged to give the same to their managers. Adopting this approach offers several benefits, such as fostering transparency and trust, and making employees feel valued and wanting to remain with the company.
Implementing data-driven talent decisions
Talent management is best powered through using data and analytics, as this can drive better decision-making and result in meaningful outcomes. By analyzing metrics like employee performance, engagement, retention rates, as well as hiring data, HR teams can arrive at informed decisions regarding talent management initiatives.
Data-driven talent management can also drive a proactive approach to the process. It means that HR teams and leaders can get ahead of the curve when it comes to looking after talent, ultimately minimizing the risk of losing talent or fighting last minute to ensure talent is looked after or retained.
Prioritizing employee development
It’s all too easy to think of employee development as an afterthought or an area of talent management that is “nice to do”. Keeping training top of mind is critical, as this benefits the employee and also contributes to the overall success of the company through motivation, reduced retention and higher productivity.
Prioritizing employee development can be achieved through creating structured learning and development programs, which can include formal training sessions, on-the-job training, taskforces, interdepartmental project work and mentoring. The messaging to employees should be to take charge of their own career development, with managers signposting and supporting where needed.
Talent management initiatives
Because talent management is so closely connected with organizational competitiveness, it pays to think outside of the box and look at things a little differently to get ahead of the game when looking after your talent. Here are three pertinent talent management initiatives to think about:
AI-based coaching
AI-based coaching is an innovative approach to talent development that blends AI and career development to offer highly personalized coaching opportunities for employees. It’s highly scalable while it can reduce the L&D workload and administration that HR teams and leaders have to deal with.
AI-powered platforms analyze performance data, as well as employee behavior patterns, and cross-match this against goals to provide real-time feedback, suggestions and actionable insights to help employees improve their skills and performance.
Furthermore, such platforms can tailor coaching sessions based on employees’ individual learning styles, challenges and competencies, providing ongoing support for career growth in a style and at a pace that suits the individual.
Diversity and inclusion initiatives
Diversity and inclusion initiatives support the creation of a workplace where employees from all backgrounds essentially feel respected, valued and taken care of. Talent management interventions in this regard include equitable access to training programs as well as career opportunities, DEI learning, affinity groups, and policies that promote DEI.
By focusing on DEI and communicating their commitment to it, employers can attract top-tier talent, diverse candidates, as well as improve innovation and drive employee satisfaction. DEI can also reduce conscious and unconscious bias in talent development, such as the hiring process and selection for promotion and training. These initiatives build a powerful employer brand, retain top talent, as well as help the company stay competitive.
Mentorship programs
Mentorship programs are a valuable resource for employee development. They can foster strong, lasting and meaningful relationships between employees (mentors) and those who are seeking guidance (mentees). To this end, mentoring helps build leadership and facilitation skills, transfers organizational knowledge, and supports career development.
In their role, mentors offer personalized one-to-one advice, share their experiences, as well as provide guidance regarding navigating the company’s culture and career paths. Mentoring doesn’t just benefit individual performance; it also directly contributes to a wider culture of sharing knowledge and nurturing each other, as well as team collaboration that strengthens the organizational culture.
Talent management examples
If you’re wondering how to get started with talent management and what to focus on as a priority, you can use these three talent management case studies as inspiration as to what works well.
Google: Data-driven talent management and employee development
Google is widely recognized for effective and innovative talent management processes. One specific area it is lauded for is a highly data-driven approach to recruit, develop, as well as retain top talent. Doing this has ensured that Google has remained one of the leading tech companies in the world for over 25 years.
One of Google’s core talent management practices is the implementation of people analytics: the collection and analysis of employee data to lead decision-making in all areas of the employee lifecycle. One initiative Google has launched is Project Oxygen, which identifies the qualities of the best leaders in the company. Data governing this is collected from analyzing feedback from staff and looking at performance metrics, thereby allowing the company to develop a framework for what makes a great and “Googly” leader.
In addition to this, Google encourages continuous employee development via its “20% Time” program, which sets out an expectation for employees to strategically spend 20% of their working hours on projects and learning outside of their regular job responsibilities, which fosters innovation as well as growth and upskilling.
IBM: AI and coaching
As a leading company in the computing space, it comes as no surprise that IBM readily leverages technology to optimize its talent management processes. One specific area that it does this is via employee coaching and development.
IBM has pioneered the use of AI-based coaching, specifically through IBM Watson Career Coach, a platform that provides personalized career development advice as well as resources to employees, making it easier for them to not only navigate but also succeed in their career paths through a large and complex organization.
IBM Watson Career Coach uses natural language processing as well as data analysis to assess employees’ current skills, their career trajectory, and development goals. Then, this information is analyzed by AI to offer personalized recommendations for training, job opportunities and learning opportunities.
In addition to this, IBM helps its employees stay competitive in the workplace through investing significantly in reskilling and upskilling its workforce. The company partners with local educational organizations to provide learning opportunities and, through IBM SkillsBuild, empowers its people to develop new skills and competencies.
Starbucks: Employee engagement and an inclusive culture
Starbucks places a strong emphasis on talent management that essentially prioritizes employee engagement as well as diversity, equity and inclusion. This permeates all stages of the employee lifecycle to create an inclusive culture where staff feel valued and supported, setting the company apart in an industry known for comparatively low job satisfaction and high turnover.
Starbucks achieves high retention and satisfaction through a few key areas. Its Comprehensive Benefits Package offers a wide range of rewards and perks, from paid parental leave to stock options, as well as plenty of learning opportunities. Connected to this is Starbucks’ College Achievement Plan, which provides full tuition coverage to eligible employees who wish to pursue a degree through Arizona State University’s online courses.
In addition to this, Starbucks makes significant efforts to foster a highly inclusive workplace through implementing a hiring and HR strategy that focuses on recruiting and promoting employees from across diverse backgrounds. It sets ambitious goals to increase the representation of women as well as ethnic minorities in leadership roles, tracking and reporting progress in these areas.
Talent management analytics
Effective talent management requires data-driven insights to measure success. Below are 15 essential analytics and metrics that are commonly used to make talent management processes as effective as possible:
- Absenteeism rate measures unplanned absences, which may indicate low engagement or workplace dissatisfaction.
- Cost per hire evaluates the total expense incurred in hiring new employees, helping with the creation of recruitment budgets.
- Diversity metrics analyze the representation of different demographics within the workforce.
- Employee engagement scores measure overall engagement through surveys, reflecting employee morale and satisfaction.
- Employee net promoter score reflects employee loyalty through their likelihood of recommending the company as a workplace.
- Employee turnover rate measures the percentage of employees leaving the organization over a specific period.
- Feedback response rates track participation in surveys or employee feedback initiatives, indicating employee involvement and trust.
- Internal mobility rate tracks promotions and lateral moves, showing career growth opportunities.
- Performance metrics measure individual as well as team achievements against clearly set goals to evaluate productivity.
- Quality of hire analyzes the performance and cultural fit of new hires to determine the effectiveness of recruitment strategies.
- Retention rate tracks the net percentage of employees who remain with the company.
- Skill gap analysis identifies areas where employee skills fall short, thus signposting towards training and recruitment efforts.
- Succession planning readiness assesses the availability of internal candidates ready and willing to fill key roles.
- Time to hire assesses the average time it takes to fill vacant positions, which indicates the efficiency of the recruitment process.
- Training completion rate tracks the percentage of employees completing assigned training programs, which highlights the impact of learning interventions.
Talent management trends
The field of talent management is ever-evolving, and it needs to be due to the competitive nature of the process and the necessity to always be on your feet to attract, develop and retain the right people. Here are some of the most current initiatives and trends in the talent management field.
AI and automation in talent management
AI and automation are changing the way talent management is approached by streamlining processes as well as enhancing decision-making. This is happening in a few different ways, such as the use of AI in recruitment to not only identify top candidates but also parse résumés as well as reduce bias.
AI coaching platforms can provide tailored development plans and real-time feedback, allowing employees to be developed more meaningfully. AI is also helpful in simplifying HR administration such as payroll and compliance management. This allows HR professionals to devote more time to high-value talent management interventions.
Finally, AI-driven predictive analytics increase the effectiveness of talent management data, allowing organizations to forestall attrition risks and future skills needs.
Data-driven decision making
Data analytics is becoming ever more powerful and decisive in talent management, offering accurate and comprehensive insights into employee engagement, performance and retention. Tools like people analytics help HR teams identify trends and act proactively in determining future talent needs and the return on investment of talent initiatives.
Real-time data can also support agile decision-making and enable companies as a whole to respond quickly to rapidly emerging workforce challenges.
Diversity, equity and inclusion
While DEI isn’t exactly a new concept for talent management, there is a growing realization that it needs to be taken to new heights as part of a truly holistic approach to looking after talent.
Because of this, companies are striving to develop more inclusive workplaces by proactively addressing hiring biases, promoting diverse leadership and fostering equitable opportunities for all employees.
As such, investing in and supporting employee resource groups can truly foster a sense of belonging, while data-driven approaches to DEI can support representation as well as equal pay goals.
Employee experience
The concept of EX has become a greater and greater driving force in talent management in recent times, as companies start to recognize and appreciate its impact on productivity, retention and engagement.
Employees are expecting organizations to provide a positive and holistic EX that focuses on meaningful work and wellbeing, and will simply work elsewhere if this isn’t provided. To improve EX, organizations are offering tools and strategies that both are relevant as well as tailored to their workforce to provide personalized experiences.
This includes mental health programs, hybrid work models and a plethora of wellness benefits. Doing this not only attracts top talent but also fosters loyalty and commitment in the existing workforce.
Upskilling and reskilling initiatives
Highly competitive talent markets and the rapid pace of technological advancements have increased the need for continuous learning as well as an equally competitive workforce. Therefore, employers are prioritizing upskilling (enhancing existing skills) and reskilling (developing new skills) to prepare their workforce to face future challenges.
Driving these efforts are investments in digital skills like data analytics, cybersecurity and artificial intelligence. These skills are being trained through advanced learning management systems, microlearning interventions, and partnering with educational organizations that specialize in such learning. These initiatives reduce the need for external hiring and strengthen the existing workforce.
Frequently asked questions
If you’re wondering where to start with adopting a best-in-class talent management strategy, then this section will cover some useful frequently asked questions.
Q: How can a small business implement talent management effectively?
Small businesses are regularly impacted by resource constraints but can still implement through adopting scalable strategies. Building a strong workplace culture should be prioritized, as should offering growth opportunities and recognition of employee contributions. All these areas can be driven in a cost-effective way. Small businesses can also use cost-effective tools such as cloud-based TMS to streamline talent management administration and reporting. Keeping open lines of communication also benefit feedback and retention of talent.
Q: How can talent management align with sustainability goals?
Talent management can back sustainability goals through incorporating green practices into the workplace. This often includes offering roles in environmental initiatives as well as promoting a culture of corporate social responsibility. Training programs can focus on sustainable business practices, whereas recruitment strategies can emphasize hiring individuals passionate about making a positive impact.
Q: What role does employer branding play in talent management?
Employer branding is an important aspect of talent management, as it refers to how potential and current employees perceive the organization as a workplace. A positive and renowned employer brand highlights the organization’s culture, values and growth opportunities, which can make it more appealing to candidates. Employer branding can be built and communicated through word of mouth, social media, and showcasing benefits. Like any form of branding, it fosters loyalty, while it can even be a source of pride for existing employees.
Key takeaways
Talent management is an important link between HR management and organizational excellence. When done right, it can offer many benefits to employees as well as the wider business.
Below are a few key points about talent management:
- Talent management covers end-to-end stages of the employee lifecycle and can be applied in many different ways.
- Talent management is increasingly being driven by artificial intelligence to help the process become easier and faster.
- Ensure you use analytics to ensure your talent management strategy can be measured.
- Follow companies and HR news to learn about companies adopting innovative talent management solutions, and follow their lead to make them work for you.
Talent management is best executed as a strategy so leaders and HR teams can focus on longer-term plans that are as good for the business today as they will be tomorrow. Take time to carefully and strategically plan out your talent management approach to make it work for your specific short- and long-term needs.
Got a question? Let us know in the comments section below.

