Poor management, as we all know, is bad for business. It lowers employee morale, increases turnover and impacts productivity, just to name a few of its effects.
Effective leadership, on the other hand, is more than good for business. For example, it increases productivity, improves communication and boosts long-term profits.
But how do effective leaders achieve this?
Well, it’s down to their management style.
In this article, we’ll explore the 10 different types of management styles, as well as their pros and cons. We’ll also look at what exactly a management style is, and how to adopt one that is right for you.
What are management styles?
Management styles refer to the specific methods and strategies that managers, supervisors and leaders adopt and implement to oversee their teams or employees. They, in essence, encompass how a manager accomplishes the objectives of their team and the company at large, makes decisions, implements plans, motivates people, organizes work, and applies authority.
While some managers use a singular management style throughout their career, others tend to switch between styles depending on a variety of factors, either in the same company or at different stages in their professional journey. Others, still, may combine two or more management styles into their way of work.
The main types of management styles
There are 10 types of management styles that are common among managers:
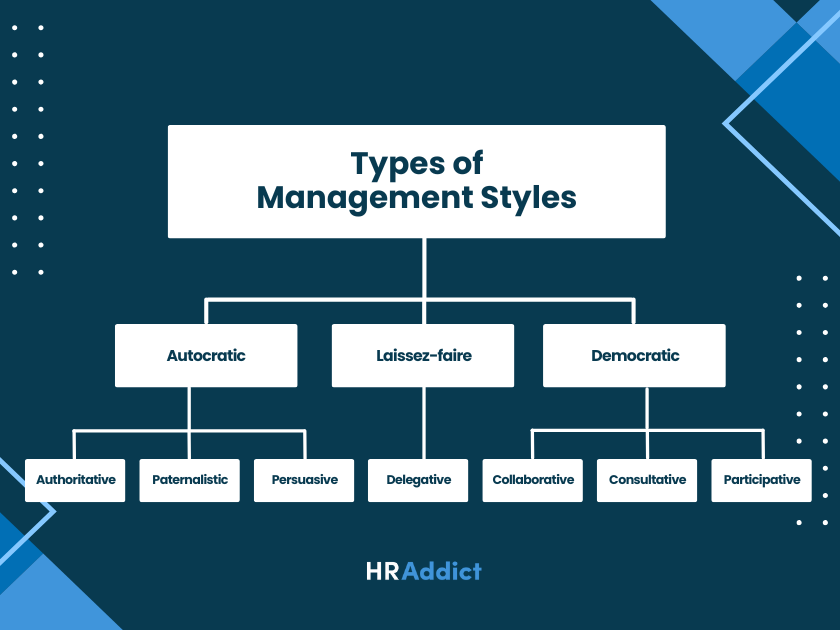
We’ll explore each management style below.
1. Autocratic management style
The autocratic style is perhaps the most controlling of all.
Autocratic managers make all decisions with little (if any) input from team members, and communication between managers and employees is one-sided, from top to bottom. To this end, however, they take full responsibility for their decisions and for handling any issues that arise independently.
Advantages of this management style include:
- Faster decision making and improved efficiency, particularly in fast-paced environments
- Improved productivity, as employees have clear instructions to follow
- Reduced employee stress and pressure, as they are allowed to complete their tasks without making complex decisions
That said, there are also some disadvantages, such as:
- Decreased employee morale, resulting from a perceived lack of trust and appreciation
- Increased absenteeism, feelings of resent, and employee turnover rates
- Amplified dependence of employees on managers, which can lead to missed opportunities in terms of new and creative ideas
2. Authoritative management style
Authoritative leadership, which extends from the autocratic management style, involves dictating orders to employees and expecting — and perhaps demanding — them to do what they’re told to do.
These employees are usually unskilled and require constant supervision, but at the same time, authoritative managers have little trust or confidence in the abilities of their team members.
There are many advantages to this management style, including:
- Clearly defined hierarchy, providing everyone with the knowledge of what they’re responsible for
- Improved short-term decision-making processes
- Improved efficiency of results, allowing team members to work towards a unified vision and shared goal
Disadvantages include:
- Decreased employee creativity, which leads to a lack of innovation
- Improved potential for micromanagement, which often results in conflict
- Increased dissatisfaction among employees, as credit usually goes towards the manager, despite their contributions to a successful project
3. Paternalistic management style
Paternalistic managers take on a parental role over their employees and focus on creating a workplace where everyone feels like family. They take care of their team and make decisions with their best interests at heart, making them one of the best types of managers.
These managers, meanwhile, will often explain the decisions they make to employees, and describe the importance of these decisions. They will generally discuss things with employees before making a decision.
Some pros of the paternalistic management style include:
- Improved employee retention, with many employees remaining in the company for most of their careers
- Improved communication lines between managers and employees
- Increased employee motivation through various incentives
Some cons, on the other hand, include:
- Increased dependence and reliance of employees on managers
- Decreased morale, especially if employees feel they’re not being taken seriously
- Increased chances of bias and favoritism
4. Persuasive management style
Another type of the autocratic management style is the persuasive manager, who makes all decisions but who shares the logic and reasoning behind those decisions with their teams, ensuring that everyone is on the same page and that employees are connected to the decision-making process.
They also focus on building on relationships with their team, and this allows them to influence and motivate them to reach their full potential.
Some advantages of the persuasive management style include:
- Improved trust between managers and employees
- Improved adaptability among employees, who become more open to change
- Higher engagement and productivity, as employees better understand the targets and goals that have been set
Some disadvantages, meanwhile, include:
- Decreased creativity among employees, as managers maintain full control over decisions
- Improved risk of confusion and tension between employers who aren’t skills communicators
- Increased sense of feeling that employees’ feedback and input isn’t being heard
5. Laissez-faire management style
The laissez-faire management style, as the name suggests in French, involves allowing employees to do what they need to do and make their own choices regarding their work.
A laissez-faire manager, essentially, takes a hands-off approach to managing employees, who don’t require supervision or much guidance, as they’re highly skilled in what they do — sometimes more skilled than the manager.
This style has several benefits, including:
- Increased autonomy among employees
- Increased creativity and flexibility among employees
- Improved career growth and skill development among team members
Some drawbacks to the laissez-faire management style include:
- Decreased cohesiveness within the team, as managers allow employees so much control and independence
- Increased sense of feeling unsupported or lost among employees
- Decreased collaboration, as the manager isn’t afforded the opportunity to lead by example
6. Delegative management style
A variation of the laissez-faire management style, the delegative management style involves assigning tasks to employees with little (if any) direction and allowing them to take full responsibility of their projects.
This type of manager is usually knowledgeable of the work and what and how it needs to be completed, and will generally only get involved during the review stage of a project.
Advantages of this management style include:
- Maximized creativity and outside-the-box thinking
- Decreased risk of micromanagement
- Improved communication and a stronger sense of appreciation
Meanwhile, some advantages include:
- Increased risk of slow productivity if employees aren’t experienced or skilled
- Increased pressure on employees, who may feel the manager is pawning all their work on them
- Increased risk of conflict if the manager’s role only exists to delegate tasks
7. Democratic management style
Also known as shared leadership, the democratic management style involves collaborating with team members and sharing the decision-making process. While the democratic manager has the final say on decisions, they encourage the contribution of their employees’ ideas.
They’re one of the best types of management styles.
There are many benefits to this style, such as:
- Improved creativity, as everyone is brainstorming ideas together
- Increased sense of feeling valued among team members
- Improved team morale and productivity
On the other hand, some drawbacks include:
- Slowed decision-making processes, as the manager listens to everyone’s ideas and opinions before reaching a decision
- Increased risk of discussions ending in uncertainty, particularly with a split consensus
- Increased sense of feeling overwhelmed among managers
8. Collaborative management style
A collaborative leader is one who collaborates with their team to make decisions and drive the business’s goals to success. They believe in their team’s abilities, and they share responsibility and accountability.
This is a relatively new management style.
Examples of advantages include:
- Improved collaboration among the team
- Expedited project delivery timelines and deadlines
- Increased sense of responsibility and ownership
Disadvantages, meanwhile, include:
- Increased rates of burnout for managers
- Increased potential of conflict between and among managers and employees
- Decreased accountability, which can lead to ambiguity and a lack of clarity
9. Consultative management style
A variation of the democratic management style, the consultative management style refers to an emphasis on team-building as well as to incorporating employees’ input into the decision-making process.
A consultative manager essentially consults employees on decisions, maintains an open-door policy, and encourages their feedback.
Some pros of the consultative management style are:
- Increased opportunities for creativity and innovation
- Increased perspectives, ideas and diverse skill sets
- Improved morale among teams, who feel valued and appreciated
Some cons, on the other hand, are:
- Slowed decision-making processes, as everyone contributes their ideas and feedback
- Increased risk of conflict among employees, particularly when an agreement can’t be made
- Decreased efficiency in decision-making
10. Participative management style
Finally, there is the participative management style. These managers are similar to consultative managers, but the marked difference exists in acting on employees’ ideas and feedback.
To ensure success, participative managers must first share all the necessary information with employees so informed decisions can be made.
This management style has several benefits, such as:
- Improved ownership of ideas among team members
- Increased employee motivation, who are able to recognize everyone’s efforts
- Improved sense of comfort sharing ideas
Meanwhile, some drawbacks include:
- Increased time costs
- Decreased accountability, as everyone has made a contribution
- Increased impracticality, particularly when important decisions need to be urgently made
How to adopt a new management style
Adopting a management style, whether it’s considered one of the “best” or “worst” ones, all boils down to whether it works for you. Once you’ve identified the right style for you, you might find the following pointers helpful in adopting it:
- Identify your current style. This will help you figure out if you really need to change or tweak it.
- Ask your team for feedback. This is essential to determine what’s currently working and what can be improved.
- Communicate effectively. Explain to your team why you’re making the change, and address their questions and concerns.
- Be flexible. If your style needs to change again, make sure to do so. Likewise, consider completing training to acquire the desired skill set necessary for your new style.
- Review your own performance. Be sure to assess your skills, strengths and weaknesses, and set goals for future improvements.
FAQs about management styles
Here are some common questions about the different types of management styles:
Q: What is the best management style to adopt?
The answer to this question is subjective and largely depends on the requirements of your position, the size of your team, the specific industry your company is in, and your own strengths and weaknesses.
Q: Can a manager have more than one style?
Yes. Some managers may combine two or more management styles into how they work. This, again, depends on a variety of factors, including the position’s requirements.
Q: How can I become a better manager?
There are many strategies you can implement to improvement your management style, such as empowering employees, becoming a better communicator, demonstrating humility, giving regular feedback and rewarding employees for a job well done.
Final thoughts
Beyond the 10 types of management styles we covered in this article, you may come across other styles which are variations or combinations. And these are perhaps the best ones. After all, great managers demonstrate a balance between more than one style and adapt to different goals as needed.
Got a question or want to share your experiences regarding your own management style? Let us know in the comments section below.
This article is a complete update of an earlier version originally published in 2017.
